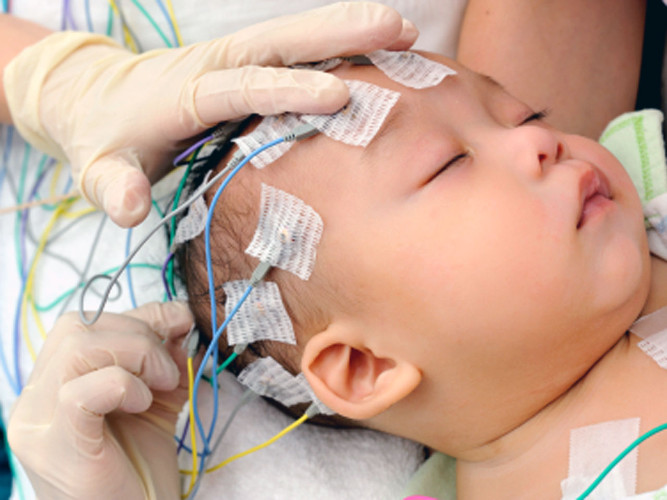
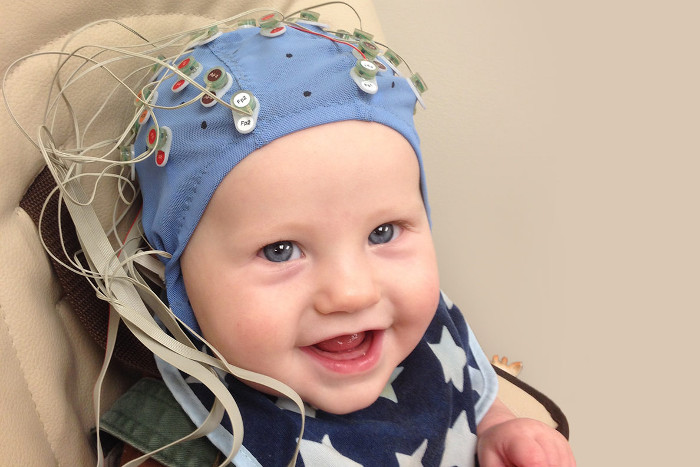
 Electroencephalogram(EEG) measures electrical activity of the brain, same as ECG which measures electrical activity of heart. It is non invasive procedure where electrodes are placed over the scalp to record electrical activity of brain. Small children may need oral sedative for the procedure.
Electroencephalogram(EEG) measures electrical activity of the brain, same as ECG which measures electrical activity of heart. It is non invasive procedure where electrodes are placed over the scalp to record electrical activity of brain. Small children may need oral sedative for the procedure.
EEG can determine changes in brain activity that might be useful in diagnosing brain disorders, especially epilepsy. It might also be helpful for guiding diagnosing like brain tumor,brain damage from head injury, brain dysfunction from variety of causes (encephalopathy), Inflammation of the brain(encephalitis) etc
 BERA(brainstem evoked response audiometry) is a non invasive objective test to determine hearing impairement in non verbal babies.
BERA(brainstem evoked response audiometry) is a non invasive objective test to determine hearing impairement in non verbal babies.
It gives the approximate average hearing threshold level. It is used to determine the degree of hearing loss objectivity in pediatric patients as well as in difficult to test patients who do not respond reliably to the subjective tests of hearing like the pure tone audiometry. It is usually done using a click sound by which the subject’s average hearing threshold across all frequencies is evaluated.
It is performed as sensory assessment of hearing for preterm babies, high risk neonates, babies with developmental delay, children who suffered meningitis etc.
 VEP(Visual evoked potential) is an evoked potential caused by visual stimulus. It measures the time for visual stimulus to travel from eye to posterior part of brain(occipital cortex). It indirectly suggest the integrity of nerves that carry the visual information from eye to the brain.
VEP(Visual evoked potential) is an evoked potential caused by visual stimulus. It measures the time for visual stimulus to travel from eye to posterior part of brain(occipital cortex). It indirectly suggest the integrity of nerves that carry the visual information from eye to the brain.
It is performed by placing few electrodes in the scalp and recorded as EEG waveform. It is advised in cases with development delay, neuroregression, vision loss etc.
 Electromyography(EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them (motor neurons). EMG results can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with nerve-to-muscle signal transmission. It is an invasive procedure where needle is inserted in the muscle and electrical activity is recorded. It is done in selective cases where the child presents with weakness of limbs, progressive difficulty in walking, suspected myotonia etc.
Electromyography(EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them (motor neurons). EMG results can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with nerve-to-muscle signal transmission. It is an invasive procedure where needle is inserted in the muscle and electrical activity is recorded. It is done in selective cases where the child presents with weakness of limbs, progressive difficulty in walking, suspected myotonia etc.
 Nerve conduction studies(NCV) is a measurement of the speed of conduction of an electrical impulse through a nerve.
Nerve conduction studies(NCV) is a measurement of the speed of conduction of an electrical impulse through a nerve.
During the test, the nerve is stimulated, usually with surface electrode patches attached to the skin. It is done in cases presenting with undiagnosed weakness of limbs, progressive walking difficulty, sensory symptoms like tingling, pain, numbness over feet and hands. Many occasions it is performed along with electromyography(EMG).
It is useful for diagnosis of hereditary sensorimotor neuropathy, guillain barre syndrome, acquired neuropathy, myasthenia gravis etc
